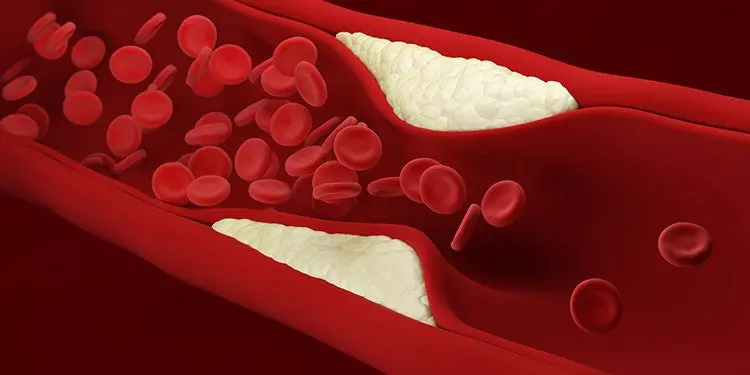
The process, which is referred to as the circulatory system, is highly dependent on the red blood cells moving freely in the arteries and veins, delivering oxygen or removing carbon dioxide so the body stays healthy, and so organs and muscles function properly. Plaque, made up of cholesterol, can build up in the arteries over time and restrict the essential flow of red blood cells so that oxygen does not get to where it is needed. This condition is called atherosclerosis and can lead to life-threatening diseases that affect the heart and even the brain.
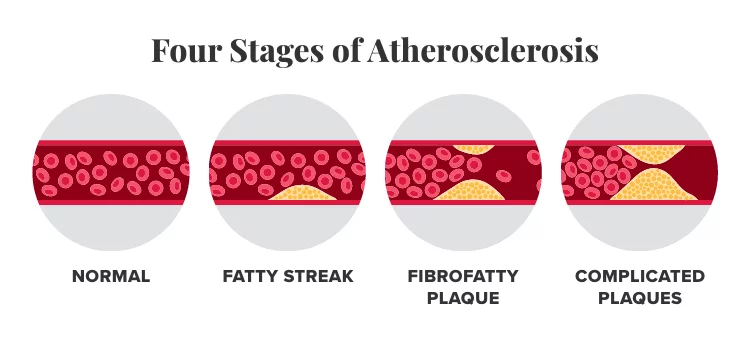
What Is Atherosclerosis?
- Fatty streak
- Fibrofatty plaque
- Complicated plaques
Atherosclerosis vs. Arteriosclerosis
Atherosclerosis Symptoms
- Chest pain
- Pain in a specific extremity
- Shortness of breath
- Becoming lightheaded or dizzy
- Confusion
- Arrhythmia or an unusual heartbeat
- Numbness
- Aneurism
- Drooping facial muscles
- Severe headache
Atherosclerosis Causes
- Diabetes
- High blood pressure
- Stress
- High cholesterol
- Obesity
- Smoking
Periodontal disease could also contribute to atherosclerosis from certain types of bacteria that enter the bloodstream through chronically inflamed gums that can ultimately cause inflammation that begins to trap plaque along the artery wall.
How Is Atherosclerosis Diagnosed?
- A stress test
- Blood tests for high cholesterol or blood sugar
- Different artery scans to look for blockage and hardening of the arteries are:
- Angiogram
- CT scan
- Magnetic resonance angiography
- Doppler ultrasound
- Ankle-brachial index that compares blood pressure taken in different extremities
- EKG
Atherosclerosis Treatment Options
- Exercise will strengthen your arteries
- Diet changes that increase healthy vegetables and are low in fat, sugar, and sodium
- Quit smoking
- By-pass surgery can be done by taking a blood vessel from another part of your body to create a new pathway around a blockage.
- Endarterectomy is the removal of plaque that builds up in your neck arteries.
- A stent can be inserted in a blocked artery to keep it open, allowing the oxygen-filled red blood cells to flow through freely.
- Thrombolytic or fibrinolytic therapies use drugs to dissolve blood clots in the arteries.
Who’s at Risk for Atherosclerosis?
- Family history
- Obesity- particularly abdominal obesity
- Diabetes
- Poor lifestyle choices like
- Consuming more than one alcoholic beverage a day
- Not eating fruits and vegetables
- Smoking
- Not exercising regularly
- High cholesterol
- High blood pressure
- Stress
What Complications are Associated with Atherosclerosis?
- Coronary artery disease can lead to heart attack, heart failure, angina, and unusual heart rhythms.
- Cerebrovascular disease leads to stroke, permanent brain damage, sight and speech disruptions, and paralysis.
- Peripheral artery disease can lead to numbness, pain when walking, and even loss of limb.
Can You Prevent Atherosclerosis?
Dietary changes
- Replacing red meat a few times a week for omega-3-rich meats like fish will benefit your health.
- Avoid fatty foods and saturated fats.
- Up the leafy green vegetables in your diet to increase your vitamin K consumption, which can keep your arteries healthy, avoiding damage. A study shows dietary nitrate-rich foods like kale, spinach, and collard greens can reduce blood pressure and improve blood vessel function.
- Increasing antioxidant fruits like berries in your diet has been shown to significantly decrease harmful low-density lipoproteins, often called bad cholesterol.
Exercise
Supplements
- Niacin is a supplement that can aid people with heart disease and has positive effects on blood clotting.
- Black tea can aid in high blood pressure and has antioxidants that can help protect blood vessels.
- Alpha-linoleic acid, which is a form of Omega fatty acid, can help maintain a normal heartbeat and can be found in walnuts.
- Garlic can help lower high blood pressure.
Find a Local Dentist
Check out The Smile Generation to find a dentist near you for all your atherosclerosis questions. You can read patient reviews, peruse staff bios, and schedule an appointment online with a click of your mouse.
Find your trusted, local dentist today!
Sources
Felson, Sabrina. "Atherosclerosis." WebMD, 1 Nov. 2021, https://www.webmd.com/heart-disease/what-is-atherosclerosis
Kapil, Vikas et al. “Dietary nitrate provides sustained blood pressure lowering in hypertensive patients: a randomized, phase 2, double-blind, placebo-controlled study.” Hypertension, 1 Feb. 2015, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4288952/
Huang, Haohai et al. “Effects of Berries Consumption on Cardiovascular Risk Factors: A Meta-analysis with Trial Sequential Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.” Scientific reports vol. 6 23625. 23 Mar. 2016, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4804301/
"Stress Managment." Mayo Clinic, 18 Aug. 2020, https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/stress-management/in-depth/exercise-and-stress/art-20044469
"Vitamins by Condition." WebMD, 2018, https://www.webmd.com/vitamins/condition-1009/atherosclerosis
Smile Generation blog articles are reviewed by a licensed dental professional before publishing. However, we present this information for educational purposes only with the intent to promote readers’ understanding of oral health and oral healthcare treatment options and technology. We do not intend for our blog content to substitute for professional dental care and clinical advice, diagnosis, or treatment planning provided by a licensed dental professional. Smile Generation always recommends seeking the advice of a dentist, physician, or other licensed healthcare professional for a dental or medical condition or treatment.