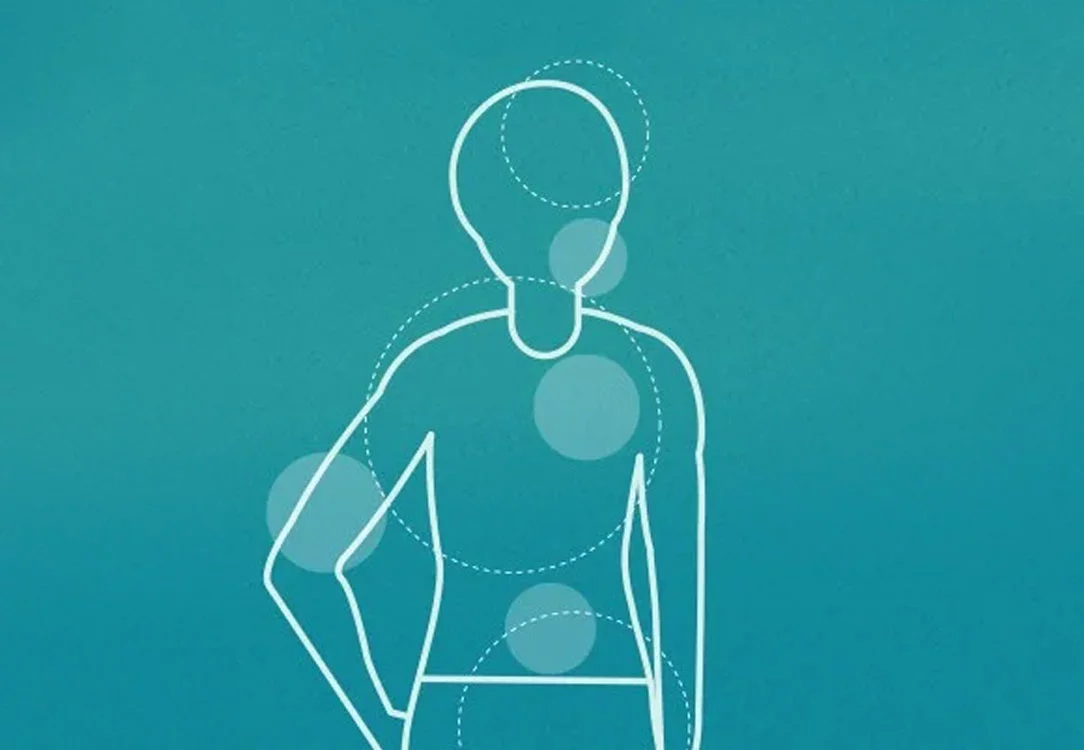
Inflammation is the root cause of most major diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, Alzheimer’s and more.
Featured Articles
You only get one set of permanent teeth, so make sure to take care of it. The rest of your body will thank you. Read the latest on The Mouth-Body Connection®.
Inflammation is the root cause of all major diseases: cancer, heart disease, and diabetes-even Alzheimer's.
Harvard Health, 2023

What is Chronic Inflammation? How to Treat it? Why is it Such a Big Deal?

Why Your Dental Health is as Important as Your Overall Health
Got questions?
Smile Generation-trusted dentists make understanding the Mouth-Body Connection simple. Call us at 1-800-SMILEGEN to get started.
Acute inflammation is site-based and situational, usually occurring due to an injury, bacteria, or toxin that has posed a threat. Chronic inflammation occurs when inflammatory cells attack a portion of the body when there is no real danger, resulting in a persistent inflammatory response. Chronic inflammation could occur for various reasons, including autoimmune disorders, long-term exposure to chemicals, autoinflammatory diseases, and acute inflammation if the original inflammatory trigger were never fully resolved. Diet and alcohol consumption, in particular, can have a major impact on the level of inflammation in the body.
Learn more in our blog article, "What is Chronic Inflammation? How to Treat it? Why is it Such a Big Deal?"
It's critical to understand not just what inflammation is but also how to spot the symptoms and what causes it in the first place, especially when it comes to chronic inflammation. You can tell if you have chronic or acute inflammation by looking at the inflammation's symptoms, length, and cause. If you have chronic inflammation, understanding the problem will allow you to take the necessary actions to treat it and return your body to its best functional condition.
Learn more in our blog article, "What is Chronic Inflammation? How to Treat it? Why is it Such a Big Deal?"
Inflammation isn't always constant; it might come and go. Acute inflammation is usually only there for as long as the damage or wound is present. The inflammation is required to allow the tissue to recover or remove the threat from the body. Although it would seem that chronic inflammation would remain constant throughout time, this is not always the case. Rheumatoid arthritis is a good illustration of this; inflammatory cells target joint tissue, causing inflammation on and off, which leads to discomfort and serious joint destruction.
Learn more in our blog article, "What is Chronic Inflammation? How to Treat it? Why is it Such a Big Deal?"
Periodontitis causes inflammation of the gums. Gum disease is mainly caused by bacteria found in dental plaque, which causes the immune system to react with an inflammatory response in reaction to germs and infection. Gum inflammation, which occurs early in the course of periodontal disease, can start the degradation of the soft tissue of the gums, which can later lead to tooth loss. However, gum disease inflammation isn't limited to the mouth. The link between gum disease and chronic inflammation can have far-reaching consequences that may surprise you.
Learn more in our blog article, "What is Chronic Inflammation? How to Treat it? Why is it Such a Big Deal?"